The chipS-CALE project develops a self-calibrating pattern to improve the measurement uncertainty of on-chip photonic sensors
Madrid / March 11, 2025
Latest news
Natural Slab Photonic Crystals as Biogenic, Customizable Nanomaterial for Label-Free Detection
Scientists demonstrate the potential of diatoms as photonic nanomaterials for sensing. The biogenic material is extracted directly from the microalgae and does not require markers, simplifying and reducing the cost of the sensor manufacturing process. Madrid / April...
The challenge of photonics
Photonics, which encompasses the generation, use and detection of light, has been identified by the European Union as a Key Enabling Technology due to its impact on sectors such as healthcare, manufacturing and efficient LED lighting. However, traditional calibration methods for optical power measurements have so far been unable to keep pace with advances in this field, especially with the trend towards miniaturisation of sensors.
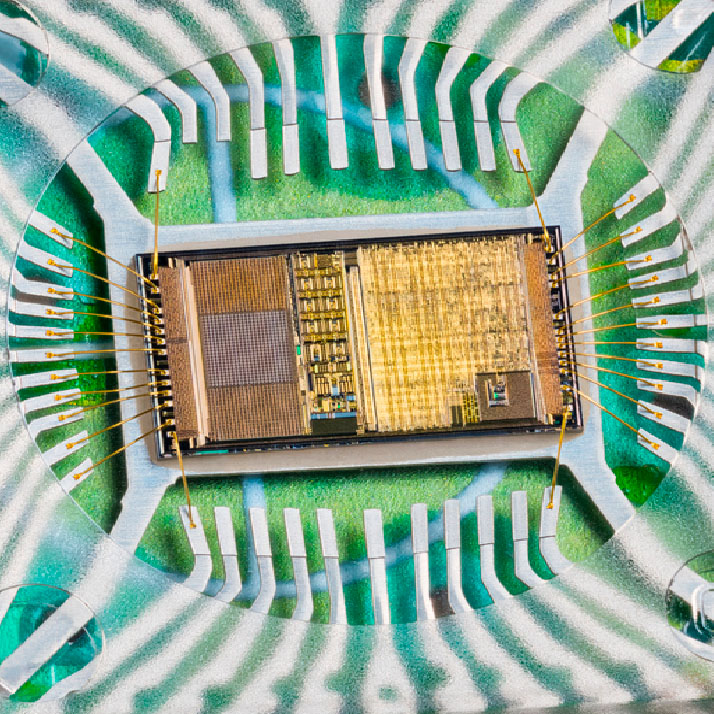
The chipS-CALE project solution
The chipS-CALE project, in which the Optical Radiation Measurements Group of the IO-CSIC participates, has researched and developed predictable quantum efficiency detectors (PQED) for use as a primary radiant flux standard, achieving record quantum efficiency and total losses of less than 10 ppm (parts per million), representing a 100- to 1000-fold improvement over previous designs.
Furthermore, the project has created the first digital twin of a PQED, allowing the estimation of the spectral response over a wide range of wavelengths (400-850) nm and simplified traceability to the International System of Units (SI).
The pattern developed on chipS-CALE is not only suitable for integration into more complex devices, but can also operate as a field sensor outside a laboratory environment, making it ideal for applications such as climate monitoring or others requiring miniaturized and high-precision sensors.
Next steps
The work carried out on chipS-CALE has laid the groundwork for the S-CALE Up project, which continues research into the development and improvement of photodetector self-calibration technologies. These advances promise to revolutionize the photonics industry, offering more accurate, precise and reliable solutions for optical measurements in a wide range of applications.
About EMPIR
The EMPIR (European Metrology Programme for Innovation and Research) is an initiative co-funded by the European Union’s Horizon 2020 programme and the participating EURAMET Member States. It aims to address key challenges in metrology and ensure that measurement science is fit for the future.
IO-CSIC Communication
cultura.io@io.cfmac.csic.es
Related news
The Institute of Optics has participated in the BxDiff project within the EMPIR program that has developed a traceable measurement system of the total appearance of surfaces with complex visual effects.
Madrid / February 27, 2023Today, research is being done in the field of metrology to develop a system for measuring the appearance of a surface,...
General V(λ) mismatch index: History, current state and new ideas
Madrid / July 5, 2023A European research team has presented a comprehensive review of the general V(λ) mismatch index and proposes new concepts for...
Online seminar by Joaquín Campos on Friday the 23rd entitled “New patterns and calibration methods to replace incandescent lamps”
Madrid / June 21, 2023Our colleague Joaquín Campos is going to offer an online conference entitled "New calibration standards to replace...





